Role of Reactors in Power Quality Management
Variable Frequency Reactors, commonly referred to as line or load reactors, are inductive components used to control current dynamics and limit harmonic interaction in power systems. Their importance has grown in parallel with the widespread adoption of power electronic converters.
Within IEC-oriented design frameworks, reactors are treated as protective and conditioning elements rather than mere accessories.
Operating Principle
A reactor introduces inductive impedance into the circuit. This impedance limits the rate of current change, reduces peak currents, and smooths waveform transitions. When applied in conjunction with Capacitors, reactors play a decisive role in preventing resonance.
In variable frequency environments, reactors help decouple sensitive equipment from upstream network disturbances.
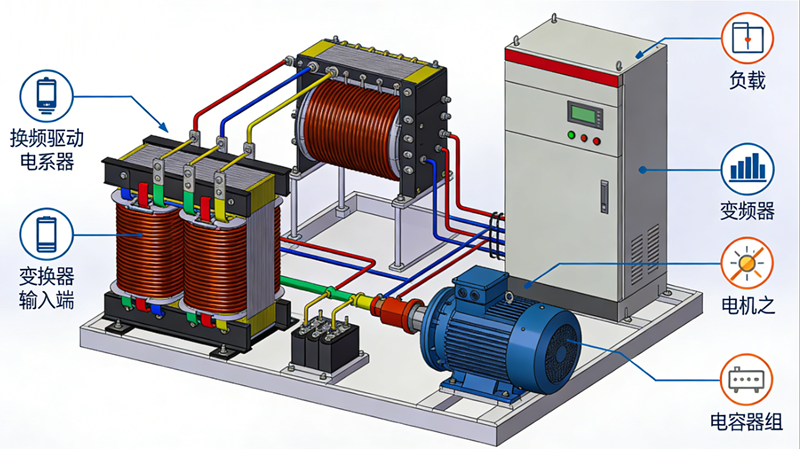
Types of Variable Frequency Reactors
Common reactor configurations include: - Line Reactors installed at converter inputs - Load reactors installed between drives and motors - Detuning reactors used in capacitor banks
Each type serves a distinct function, although their electromagnetic principles are similar.
System-Level Benefits
Properly applied reactors contribute to: - Reduced harmonic current injection - Improved voltage waveform quality - Lower thermal stress on converters and motors
These benefits translate into enhanced reliability and compliance with power quality standards.
FAQ
Does adding a reactor increase energy losses?
Yes, marginally. However, these losses are typically outweighed by reliability gains.
Are reactors required for every VFD installation?
Not universally, but strongly recommended in weak or harmonic-sensitive networks.

 English
English
 Español
Español
 Portugues
Portugues
 Pусский
Pусский
 Français
Français
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 日本語
日本語
 한국어
한국어
 العربية
العربية
 Italiano
Italiano
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 Svenska
Svenska
 Polski
Polski
 Türk dili
Türk dili
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Melayu
Melayu
 dansk
dansk
 Magyar
Magyar
 қазақ
қазақ
 বাংলা
বাংলা
 עִברִית
עִברִית
 čeština
čeština
 українська
українська
 беларускі
беларускі
 Suomalainen
Suomalainen
 اردو
اردو
 հայերեն
հայերեն
 български
български
 Hrvatski
Hrvatski
 galego
galego
 नेपाल
नेपाल
 euskara
euskara
 Shqipëria
Shqipëria
 Malagasy
Malagasy
 Башҡорт
Башҡорт
 Türkmenler
Türkmenler
 Ilocano
Ilocano
 Нохчийн
Нохчийн













 Whatsapp
Whatsapp Telepono
Telepono
Magkomento
(0)